Basic Principles

Chapter 1
The Society Organism →

Chapter 1b
The Levels of Human Mentality →

Chapter 1b
What is a Society, Nation, and State? →

Chapter 1c
The Essentials of a Civilization →

Chapter 3
The Common Interest as The Conscience of Society →

Chapter 3b
Self-Regulation Requires Fellow-Feeling →
Chapter 4
What is Morality? →

Chapter 4b
What's the Difference Between Reasonable vs Unreasonable? →

Chapter 4c
'God and Morality →

Chapter 4c
The Four Generation Rule in Families →
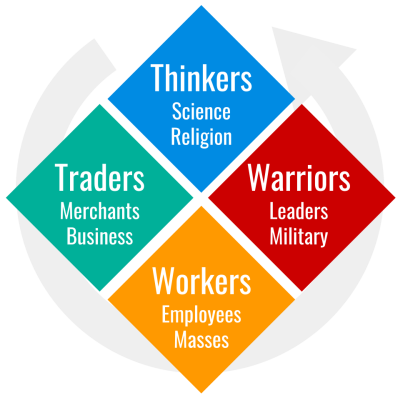
Chapter 5
The Law of Social Cycles by Socrates →

Chapter 6
What is Social Topographic Behavior? →






