Space And Time In Classical Mechanics
3 minutes • 427 words
The purpose of mechanics is to describe how bodies change their position in space with time.
What does “position” and “space” mean?
I stand at the window of a railway carriage which is travelling uniformly.
- I drop a stone on the embankment, without throwing it.
- Disregarding air resistance, I see the stone descend in a straight line.
- A pedestrian on the footpath sees this and notices that the stone falls to earth in a parabolic curve.
Do the “positions” traversed by the stone lie on a straight line or on a parabola?
What does motion “in space” mean?
We should entirely shun the vague word “space”.
- We replace it with “motion relative to a body of reference.”
- We then replace this “body of reference” with “system of coordinates.” This will allow mathematical descriptions.
In this way:
- relative to a system of coordinates rigidly attached to the carriage, the stone travels at a straight line
- relative to a system of coordinates rigidly attached to the ground (embankment), the stone travels in a parabola
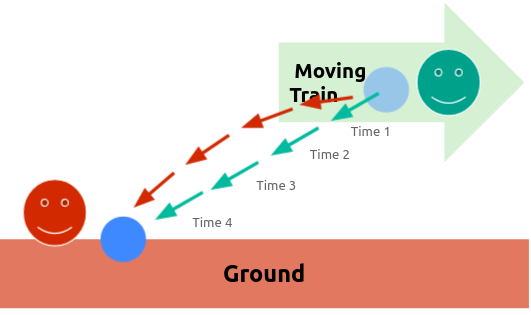
This shows that there is no such thing as an independently existing trajectory. Instead all trajectories are relative to a viewpoint.
A complete description of a body’s motion must specify how that body changes its position with time. For every point on the trajectory, the time of the body must be stated. Such time-values are then the magnitudes (results of measurements) capable of observation.
Under Classical mecahnics, we imagine two identical clocks.
- One is held by an observer in the railway-carriage window
- The other is with an observer on the footpath
Each of the observers determines the position of the stone from his perspective at each tick of his clock.






