What Gives Objects Their Weight?
Table of Contents
What is the weight of this physical Earth?
The weight of the Earth is caused by the force that unites all its particles and makes them all tend toward its center, according to their:
- size and
- solidity.
This force is made up of the air-aether of the planetary gravitational territory surrounding it.
- This air-aether farther from the center rotates faster than the air-aether inside the Earth.
- This faster speed causes them to move away from its center with more force.
- This then pushes the earth-aether back toward its center.
In previous chapters, I said that:
- the most massive and solid bodies, such as comets, tend to move outward towards the edges of the stellar gravitational territory.
- the less massive and less solid ones are pushed back toward the centers of that territory.
This makes it appear contradictory to what I am saying about the particles of the Earth.
But this assumes that they were already moving with the same agitation as the air-aether of that stellar gravitational territory.
It does not follow that:
- the less solid parts of the earth-aether could be pushed back towards its center.
- the more solid ones should move away from the center.*
Superphysics Note
In reality, the earth-aether would be pushed towards the center towards the direction where the air-aether were turning if:
- the earth-aether had not yet moved, or
- the earth-aether moved slower than what is required* to follow the air-aether
Superphysics Note
The air-aether will push the earth-aether with more force and speed the larger and more solid the earth-aether is.
Nevertheless, the earth-aether in comets can move towards the exterior of the stellar gravitational territory.
- This is because they gained speed by going towards the center of the solar system.
- This will give them enough force to pass beyond the exterior upon their exit
The earth EFGH and its water 1234 and air 5678 are a single mass.
- Its water and air are composed of the less solid of the earth’s parts.
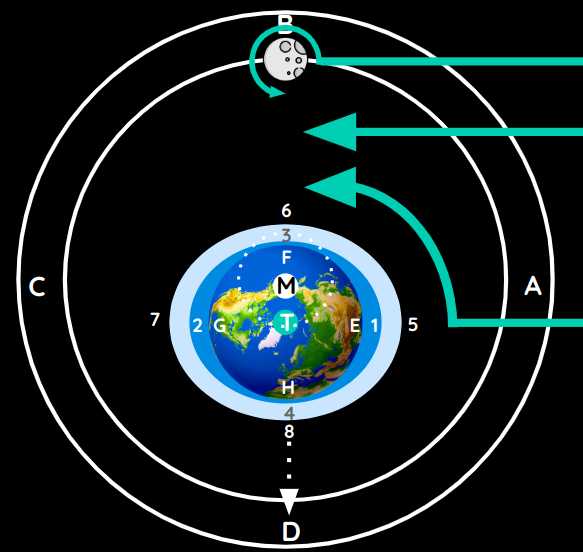
The air-aether fills:
- all the space between the circles
ABCDand5678, and - all the small intervals below it among the parts of the air, the water, and the earth.
This air-aether and the Earth turn together around center T.
All their parts tend to move away from that center.
- The air-aether outside of Earth moves away faster than the air-aether within the Earth because the former are much more agitated.
- Likewise, the parts of the Earth that are more agitated in the same direction as those of the planetary gravitational territory tend more to move away from the center than the less agitated.
“Void” here means the space that is filled only with pure aether that could not resist the actions of other bodies nor produce any considerable effect.
If the whole space beyond circle ABCD were a void, then all the parts within the circle ABCD would be the first to leave it.
- It would be followed by those of the air
- It would then be followed by those of the water
- Finally it would be followed by those of the earth
Each of them would follow much sooner as it were less attached to the rest of its mass.[51]
Gravitational Equilibrium
There is no void beyond circle ABCD.
This means that the air-aether inside it has nowhere external to go to unless the external air-aether goes in simultaneously.
Similarly, the earth-aether also cannot move away any farther from center T unless air-aether or earth-aether descend in their place.
They also cannot move closer to the center unless just as many others move out from the center to be replaced.
Thus, they are all opposed to one another.
Each opposes:
- those that must enter in its place in the case that it should rise, and
- those that must enter therein in the case that it should descend
This is similar to how the 2 sides of a balance are opposed to one another.
One side of a balance can be raised or lowered only if the other side does exactly the contrary at the same instant.
The heavier side of the balance always raises the lighter side.
