The Fourth Law of Value

Chapter 1
The Third Law of Value →
Chapter 1b
Dharma as the Natural Organizing Principle →

Chapter 1c
Free Competition →

Chapter 2b
The Fallacy of Liquidity Preference →

Chapter 3
Three Modes of Exchange →

Chapter 3b
The 3 Problems with Money →
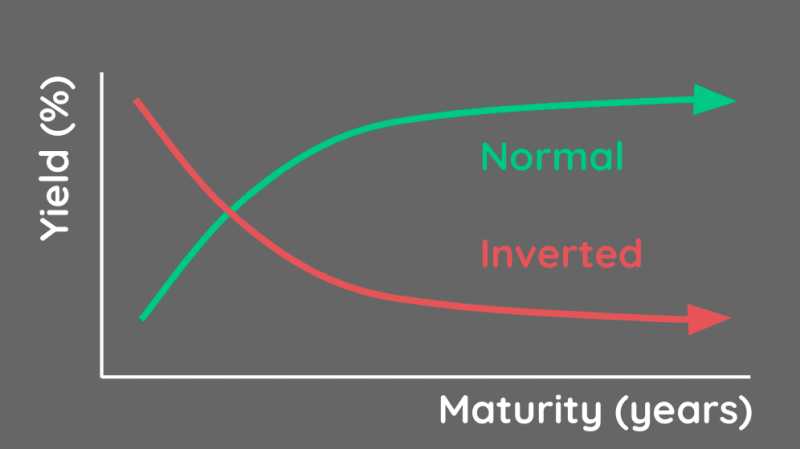
Chapter 5b
Government Bonds and Bond yields →

Chapter 7
The Four Revenues: Rent, Wages, Profits, Donations →

Agreeableness, Difficulty, Constancy, Trust, Success
The 5 Factors that Affect Wages and Profits →

Chapter 7c
Interest Rates →

Chapter 7d
Profit Maximization and the Cycle of Poverty →
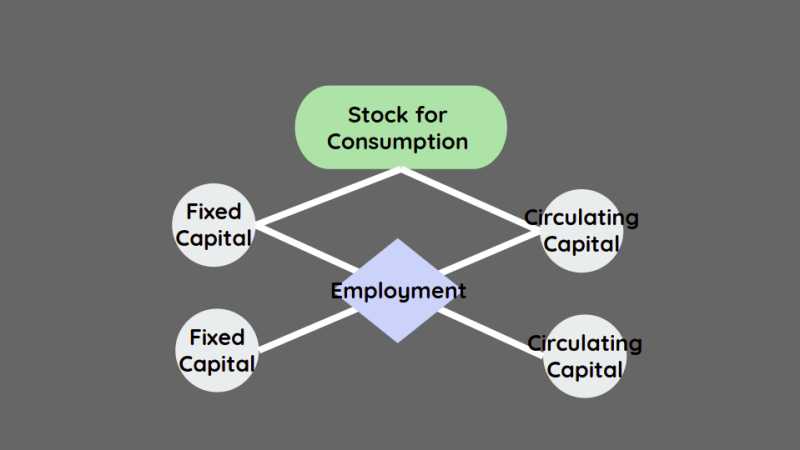
Chapter 8
The Modern Economic Table →






