The Convertible Layer of Superphysics
The Convertible Layer is the fourth layer. It reconfigures the radiant layer in order to produce diversity in the material layer.
| Attribute | Quality |
|---|---|
| Name | Conversion |
| Physics Name | Weak Interaction |
| Traditional Name | Water, Jala, 土 |
| Descartes’ Name | included in the 1st Element |
| Domain | Physical |
| Force | Change |
| Medium | W and z bosons, intramolecular and intermolecular forces |
| Substance | Neutron, High energy Neutrinos |
| Quanta | Neutrino (qoc1) |
| Aether Content | 2 |
| Movement | Mostly Kinetic |
It manifests as radioactivity, chemical change, flavor changing, and is governed by the ‘Weak Force’ and graphically through Feynman diagrams.
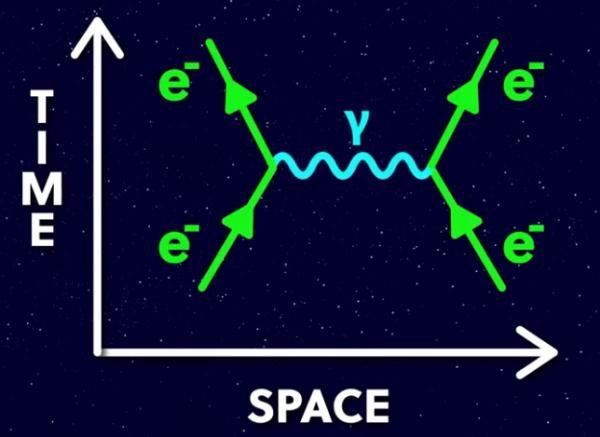
While the radiant layer is the basis of electricity, optics, and electronics, and thus the electronics and computing industries, the convertible layer is the basis of chemistry, and thus the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
In terms of creation, this is the fourth layer that processes energies and matter into other kinds.
Definition of the Convertible Layer
This layer creates the diversity in the material universe arising from the inherent instability of the convertible layer because of its position in the 5 Elements hierarchy which gives it 2 aether particles in our Law of Conservation of Aether or Substance.
This is because 3 is the minimum number for stability in the logic of Aristotle, Socirates, and Vedas (i.e. there are 3 gunas).
This instability has both dynamic (very unstable) and static (least unstable) parts.
This lets it convert other particles, both radiant and material.
This layer was traditionally associated with water and liquids because they are always moving and can switch between gas, liquid, and solid.
The importance of liquids in Conversion is seen in convertible quanta, as neutrinos, being detectable in liquid argon and chlorine.
The conversion layer leads to chemistry, and bio-chemisty and organic chemisty when merged with Bio Superphysics.

The ability of this layer to facilitate between the static material layer and the dynamic radiant layer makes it very useful for reactions.
This is seen in gunpowder (which Taoist science attributed to the water element) and in Element 115 which according to Bob Lazar converts to Element 116 which then converts into antimatter for portable energy.