Radiant Relationalities
Particle spin is the orientation direction of a particle.

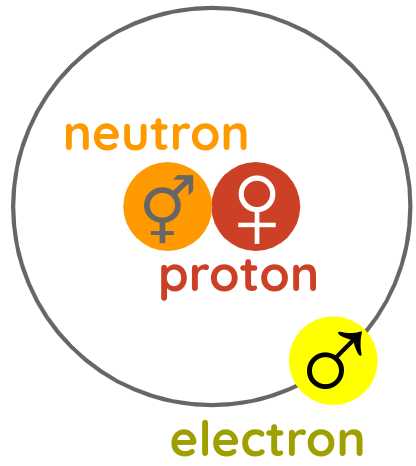
Male and Female Polarity Instead of Charges
Section 1

Radiant Spin: Right Handed Threads
Section 2

How Quantum Spin was Invented
Section 3