Colors: Prisms and LEDs
Colors are from the anticlockwise spin of photons.
- A vortex-less or spin-less light-wave or group of photons is called ‘white’.
- A lightwave or bunch that is absorbed instead of being reflected is called black.
A lightwave or photon group becomes colored by adding an anticlockwise vortex or spin to it.
- A fast photon spin is called red. It travels at 700 nanometers per time unit. We say it is fast going to matter
- A slow photon spin is called blue. It travels at 450 nanometers per time unit. We say it is slow going to matter
This spin can be imparted in 2 ways, based on origin:
- Colors from matter activity
This is from stars and flames where the sources are protons.
- Colors from spatial activity
This is from LEDs, prisms, and rainbows. These are from refraction of light through:
- angled surfaces such as prisms and LEDs
- curved surfaces such as droplets which show colors as rainbows
Prisms
A prism creates colors by adding a vortex or spin to mors by slowing it down.
In the image below, the light wave enters through the prism flat. However, the wave exists the prism at different lengths.
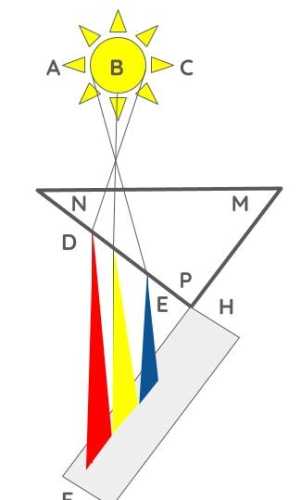
The right side goes through more prism which makes it slower relative to the light waves on the left which passes through less prism.
- This makes the left side red and the right side blue.
Light-Emitting Diode or LED
An LED is a metal that converts virtual photons in to colored photons.
This is done by creating channels for electrons (‘minutiae’ in Cartesian Physics) to flow while spinning since electrons and photons are vortices.
An n-type semiconductor has an oversupply of electrons. This goes to a p-type which has a hole for that electron.
Within a semiconductor is a band gap where electrons can switch lanes as they flow from n to p.
The virtual photons (‘striated particles’ in Cartesian Physics) in the band gap go through the spinning electrons as they switch lanes.
If the electrons flow as tight channels, the virtual photons would become dense. This creates magnetism that would push space particles.
But since the electrons that cross the band gap are not tight, the virtual photons are less compressed. And so they become photons instead of causing magnetism.
A red LED has a small band gap that acts as a spatial prism. This lets the photon pass quickly, causing red light.
A blue LED has a large band gap. This lets the photon pass slowly, causing blue light.
In theory, an electron that changes lanes in a 90 degree angle would give off white light just as a light that passes through a flat glass will come out the same white.
So in theory, Superphysics can lead to real-definition LEDs that exactly match real life visual crispness.
That 90 degree sudden shift is like a car switching lanes instantly. That can only be done by application of the aether, as in all cases that require violations of spacetime.
Star Colors
The colors that come from stars are sourced from the relation of their proton and the heat energy in their aetherspace.
A hot star will have more radiant energy and subsequently less matter or heavy protons. This will create a white or blue color.
A cooler star will have less radiant energy and more matter as heavy protons. This will create an orange or red color.
The space around Earth has variations. But space around stars has no variations.
This is why:
- there is green and UV LED but no green or violet star
- there is no white LED but there are white stars
Since red stars are fast going to matter, then it has less energy and less heat. Blue stars are slow going to matter and so have more energy and heat.