Spatial-Radiant Relationality
Table of Contents
The pervious part explained the essential ingredients for Einstein’s Special Relativity.
| Einstein Concept | Meaning |
|---|---|
c |
A constant to create patterns |
| Simultaneity of time | creating movement within those patterns |
| Minkowski space | a space that allows c-based patterns and time |
| Metric Tensor | Plotting tiny movements in the Minkowski space |
These included key fallacies which actually trap reality within the radiant layer.
- the application of the constant sped of light c onto space
- the confining of time with that same c as the ‘simultaneity of time’
These led to sub-fallacies:
- Minkowski spacetime
- Metric Tensor
Material Superphysics flips some of these concepts in order to allow reality to break out of the radiant layer and into the spatial and aeterheal layers.
| Einstein Concept | Material Superphysics Replacement |
|---|---|
| Minkowski space | 7 dimensions |
| Metric Tensor | 2D Space-Time slices |
Specifically, we fixed them by:
- applying c onto particles as particle-shapes instead of applying it onto space
- removing the reality of the ‘simultaneity of time’ and instead keeping it a human policy for analyzing certain phenomena
- replacing the Minkowski spacetime with 2D spacetime slices, and the Metric Tensor with the timespace particle
We deny the simultaneity of time as a real phenomenon and instead see it as the desire of the measurer to have a definite answer. For example, instead of getting the answer 1.12345 in one time, 1.1234 at another, and 1.123 at another, we can set it to a standard 3 decimal places to always come up with 1.123.
For judging space, the timespace particle becomes the most important concept, especially since it is in the upper spatial sublayer close to the aethereal layer. This replaces mass in Newton’s system and the stress-energy tensor in that of Einstein.
Spatial-Radiant Relationality as General Relatvity
Here, we explain the Spatial-Radiant Relationality which is roughly similar to General Relativity of Modern Physics.
Since humans have spent a lot of effort exploring General Relativity, we will use the data and equations from it, and then convert it to Cartesian.
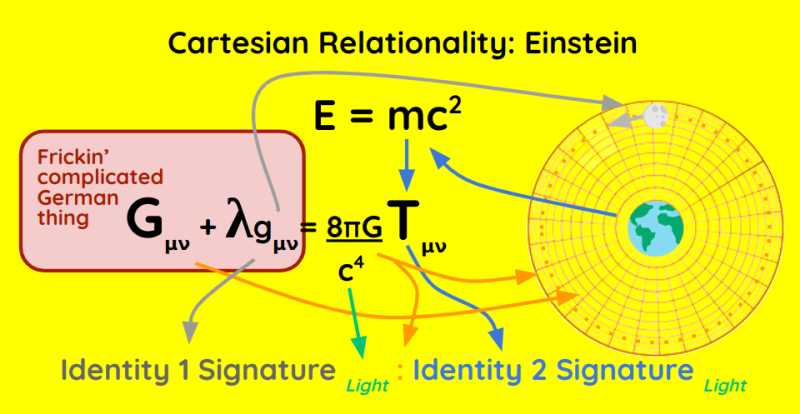
As mentioned in the previous part, the main mechanism of General Relativty is the stress-energy tensor, just as that of Special Relativity is the metric tensor. Rather, the stress-energy tensor adds features for the metric tensor by adding curvatures.
These curvatures are then the map where the moving object will go through.
Comparing Einstein with Newton and Descartes gives us:
| Einstein | Newton | Descartes |
|---|---|---|
| Metric Tensor + Cristoffel Symbols | Orbit edge | 2D Spacetime + Timespace1 |
| Stress-Energy Tensor | Mass | Timespace2 |
| Riemann Curvature | Orbit interior | Relational differences between Timespace1 and Timespace2 |
As you can see, the Riemann Curvature, as the warping of spacetime, is the most complicated part of General Relatviity just as the relational differences between Timespace1 and Timespace2 are to Cartesian Relationality.