Galaxies and Quasars
Table of Contents
Galactic qosts manifest as either galaxies or quasars.
| Qost | Rotation | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Galaxy | Anticlockwise | Convert energy into matter |
| Quasar | Clockwise | Convert matter back to energy |
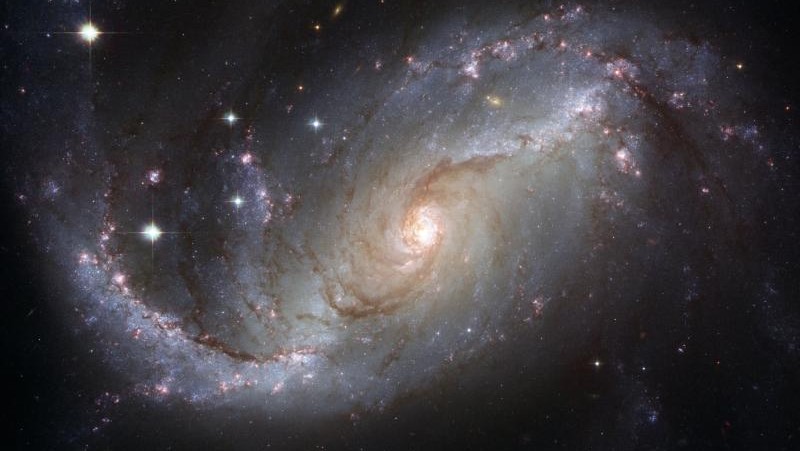

Galaxies convert energy into matter, as stars and planets, just as quasars convert matter back into energy.
- This prevents the universe from having a thermal death.
Galaxies
The structure of a galaxy depends on the rotation and energy of its vortex.
According to Descartes, a galaxy forms when mosts (which he calls the 2nd Element) collide with other mosts to form vortices which we call sos'.
- The weaker and smaller ones revolve around the larger and stronger ones.
- These larger ones are naturally separated by their mutual repulsion from the need to retain their uniqueness.
At the beginning, God placed every sort of inequality among these particles. They had all sorts of sizes, shapes, and dispositions to move or not to move, in all ways and in all directions. But that does not prevent them afterwards from having been rendered almost all fairly equal, especially those that remained an equal distance from the centers around which they were turning.
Thus, in a short time, all the parts were arranged in order. Each became more or less distant from the center around which it had taken its course, according as it was more or less large and agitated compared to the others.
Rene Descartes
The World Simplified
These vortices swirl as galaxies, just as cold and warm air create typhoons and tornadoes.
- The more warm air is present, the stronger the typhoon becomes.
- Likewise, the more Positive aether is behind the compiled ideas for a galaxy, the larger its area of influence, when it turns into a spiral galaxy.
| Type | Age | Size |
|---|---|---|
| Irregular | Young | Small |
| Spiral | Medium | Medium |
| Lenticular | Medium | Medium |
| Elliptical | Old | Large |
A galaxy is therefore created in the following steps:
- The Supreme has an idea for a universe
- The Aether gets the ideas for that universe, packages them as organized ideas (qoa) for distribtion to spacetime (spatial layer)
- Galactic mosts and sos emerge in the spatial layer as irregular galaxies. These repel each other to create space
- The positive aether acts on the galactic sos to create smaller vortices, as stellar qosts
- Stellar qosts emerge within this area to convert energy into matter which are then spread via supernovae, and life through their Positive Force (Living energy is in the spatial Air Element)
- The galactic qost runs out of ideas (and feelings), leaving its stars behind as globular clusters.
- The stars die and become pure space
As you can see, galaxies produce solid matter as planets through their stars. In time, this would cause the universe to have more matter and so lose energy.
Quasars are Reverse Vortices
To prevent this, some qosts rotate in the opposite direction as quasars. This converts matter back into energy, reversing the process.
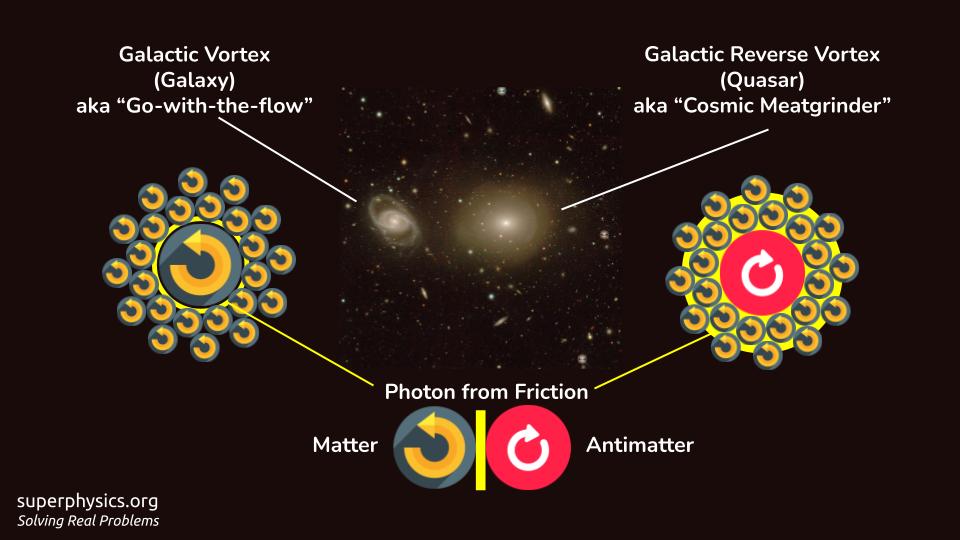
When a large powerful clockwise vortex touches a small anticlockwise vortex, the latter does not go with the former, as in a galaxy.
Instead it stays in stasis around the large vortex similar to 2 gears staying at the same spot.
Other particles join in, creating large stasis similar to a traffic jam.
In time, more particles get snagged in this traffic jam, leading to a pileup that compresses the particles sequentially like a meatgrinder.
This leads to friction that creates much more light than a galaxy.
In time, matter as planets, asteroids, comets etc get snagged, crushed and spit out back as light and energy to be sent far away.
This de-crudifies energy and re-energizes the universe.
It follows that that the ratio of galaxies and quasars should be roughly similar. It means that some bright galaxies should be reclassified as quasars.
These may be elliptical like normal galaxies but are distinguished by the lack of arms or distinctive features because of the difference of the motion of the parts and the center.